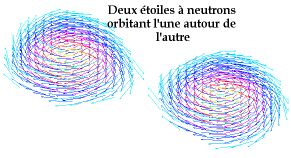
The picture above shows the velocity field seen by an observer following the orbital movement during the final phase.
3. Binary system of neutrons stars (Silvano Bonazzola, Eric Gourgoulhon, Jean-Alain Marck)

The picture above shows the
velocity field seen by an observer following the orbital movement
during the final phase.
The fluid is not at rest in this frame, because the rotation is not rigid (the flow is assumed to be irrotational). The upper half (above the orbital plane) of the stars is represented. The color code corresponds to the density.
Glossary:
Einstein equations: describe the evolution of the gravitational field in the theory of general relativity. In Newton's theory, stars move in Euclide's space, in a gravitational field which they generate themselves. In Einstein's theory, stars move without external forces in a curved space, the curvature being again generated by the stars: the space curvature replaces the gravitation. In the limit of slow curvature, this is the same.
conformally flat: a special (relatively simple) geometry of space, which allows to solve only 5 of the 10 Einstein equations.
neutrons stars: very dense stars made almost entirely of neutrons - a pulsar is a neutron star. The equilibrium is reached by a balance between gravitation and the strong force between neutrons. A neutron star is the remnant of the core of a massive star after a supernova explosion. Its mass is close to that of the Sun, and its size comparable to a city (like Paris). The density within such stars is larger than the density within the atomic nucleus, 10^17 kg/m^3.
gravitational waves: gravitationnal equivalent to electromagnetic waves. Could be emitted by stars orbiting very close one to the other - not yet detected. In Einstein's theory, these waves are "space-time waves".
gamma bursts: could be the signature of very close binary systems.
black hole: still more compact than a neutron star. A black hole is (as a neutron star) the remnant of a supernova explosion, when the initial mass of the star is too large; in that case, the strong interaction is unable to fight against gravitation, so that the collapse if even more dramatic. The black hole is separated from the rest of the universe by an immaterial boundary called the horizon, that nothing (even light), can cross in the outside direction.